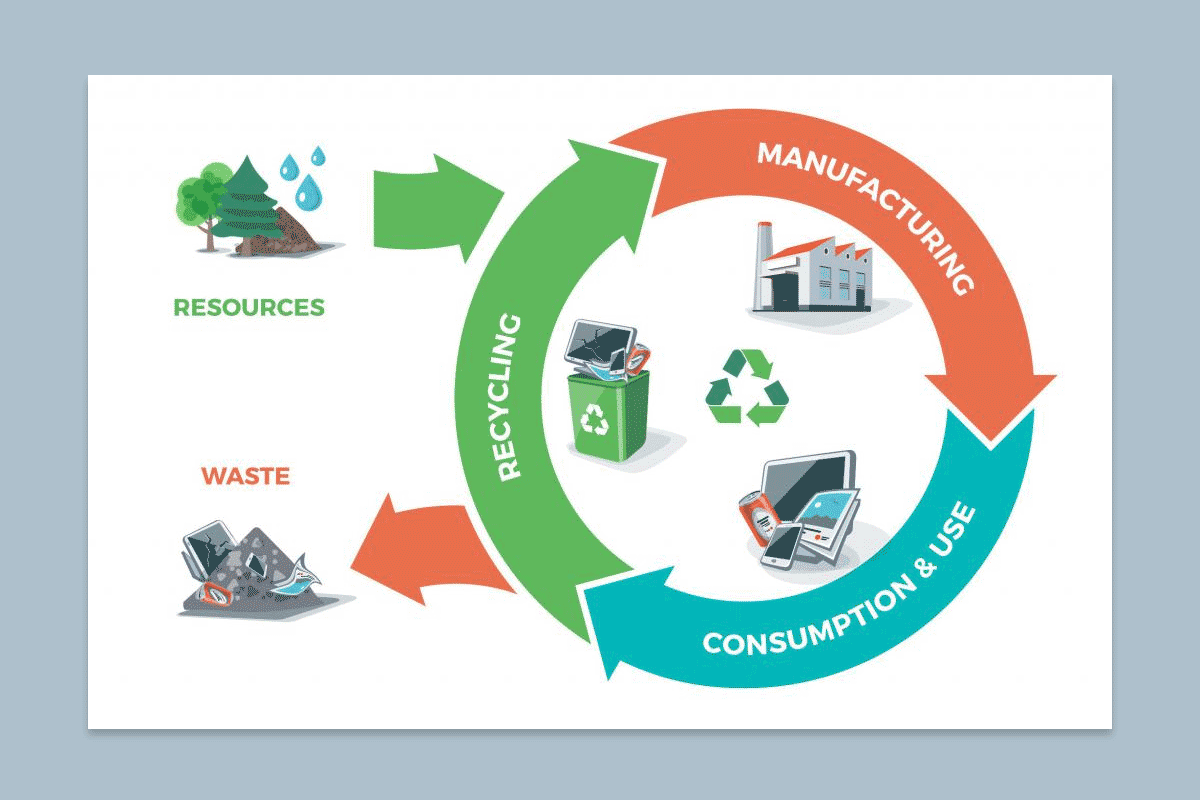
In the fast-evolving landscape of technology and innovation, Technical Masterminds are at the forefront of designing and manufacturing processes that not only push the boundaries of what is possible but also prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles. This article delves into the ways these visionary minds are reshaping industries by incorporating eco-friendly practices into their designs and manufacturing methods.
Understanding the Need for Sustainable Design in Technology
In this section, we explore the growing awareness of the environmental impact of technological advancements and the need for sustainable design. Highlighting the shift in consumer preferences towards eco-friendly products and the role of technical masterminds in meeting these demands.
Key Principles of Circular Economy in Engineering
This section provides an in-depth look at the core principles of circular economy and how they can be applied in engineering. Topics covered include the importance of resource efficiency, product life extension, and the reduction of waste in the design and manufacturing processes.
Designing for Durability and Reusability
Technical masterminds are increasingly focused on creating products that are durable and can be easily disassembled for repair or recycling. This heading explores the strategies and technologies used to design products with extended lifecycles, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Sustainable Materials Selection and Innovation
Examining how the choice of materials plays a crucial role in sustainable design, this section discusses how technical masterminds are opting for eco-friendly materials and fostering innovation in material science. Insights into the development of biodegradable plastics, recycled metals, and other sustainable alternatives are explored.
Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing Processes
Efficient energy use is a cornerstone of sustainability. This section delves into how technical masterminds are implementing energy-efficient practices in their manufacturing processes, from optimizing machinery to adopting renewable energy sources, thereby reducing the carbon footprint of their operations.
Embracing the Internet of Things (IoT) for Sustainability
The integration of IoT technology in products and manufacturing processes is explored in this section. Technical masterminds are leveraging IoT to optimize resource utilization, monitor energy consumption, and enable predictive maintenance, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient production ecosystem.
Collaboration and Industry-wide Initiatives
Highlighting the collaborative efforts within the industry, this section discusses how technical masterminds are joining forces with other companies, research institutions, and government bodies to promote sustainability. Initiatives such as shared resources, open-source designs, and knowledge-sharing platforms contribute to a collective commitment to a circular economy.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Outlook
Addressing the challenges faced by technical masterminds in implementing sustainable practices, this section explores potential solutions and outlines the future outlook for sustainable design and manufacturing. Topics include regulatory support, consumer education, and the role of emerging technologies in overcoming obstacles.
Conclusion
This article underscores the pivotal role of Technical Masterminds in driving the integration of sustainability and circular economy principles into the heart of design and manufacturing processes. By embracing these practices, the engineering community is not only contributing to a healthier planet but also shaping a future where technology coexists harmoniously with the environment.
- Does PRMovies offer subtitles for movies? - March 3, 2024
- Are there any age restrictions for using Rdxhd? - February 29, 2024
- How Do Technical Masterminds Incorporate Principles Of Sustainability And Circular Economy Into Their Design And Manufacturing Processes? - February 23, 2024